nodejs 和 pm2 安装配置
Node.js 是一个 基于 Chrome V8 引擎的 JavaScript 运行环境,可以让 JavaScript 在服务器端运行 。
- JavaScript : 原本只能在浏览器运行
- Node.js : 让 JS 可以读写服务器
Node.js 的核心特点:
- 单线程模型 ,通过 事件循环(Event Loop) 实现高并发。
- 非阻塞 IO ,适合 IO 密集型任务,不适合 CPU 密集型任务(单线程一旦被卡住,整个服务器就会卡住)。
- npm 生态 ,
npm是世界最大的包管理平台。
Node.js 安装
wget https://nodejs.org/dist/latest/node-v15.12.0-linux-x64.tar.gz |
安装pm2
npm install pm2 -g |
Node.js 相关常见操作
安装包
npm install pm2 |
安装指定版本的包
npm install -g [email protected] |
查看可用的安装版本
以 hexo 安装包为例,以下命令查看 hexo 安装包有哪些可选版本
npm show hexo versions |
查看已安装的包名
以下命令可显示安装的包及它们的版本
npm ls |
如果要查看全局类型的包,使用 -g 选项
npm ls -g |
卸载安装的包
npm uninstall package_name |
卸载全局安装的包
npm uninstall package_name -g |
Node.js 常见错误
WARN EACCES user “root” does not have permission to access the dev dir “/root/.node-gyp/11.15.0”
ERR! stack Error: EACCES: permission denied, mkdir ‘node_modules/sqlite3/.node-gyp’
[解决方法]:
npm install --unsafe-perm |
Node.js 基础项目结构
一个 Node 项目通常是:
project |
在 Node.js 生态中,通常有两个 核心基础配置文件
- package.json : 这是每个 Node.js 项目的核心。它定义了项目的元数据、依赖项和运行脚本。
- .env : 我们绝不应该把数据库密码、API 密钥等敏感信息直接写在代码里。通常配合
dotenv库使用。
package.json 配置文件详解
{ |
name&version: 项目名称和版本。发布npm包时这是必填的唯一标识。main: 程序主入口,Node 默认的执行文件。scripts: 这是整个配置中最重要的部分。它定义了 快捷命令(命令脚本) :"start": "node app.js"-> 执行npm start命令,实际会运行node app.js启动程序。"dev": "vue-cli-service serve"-> 执行npm run dev命令,会使用vue-cli-service serve启动服务
dependencies: 行环境必需的包(如express, mongoose等)。安装命令:npm install <pkg>。devDependencies: 仅开发环境需要的包(如eslint, jest, nodemon)。安装命令:npm i <pkg> -D。engines: 指定 Node.js 或npm的版本范围,防止因环境版本不同导致代码崩溃。
初始化项目 ,会生成 package.json
npm init |
安装依赖
npm install |
启动
node app.js |
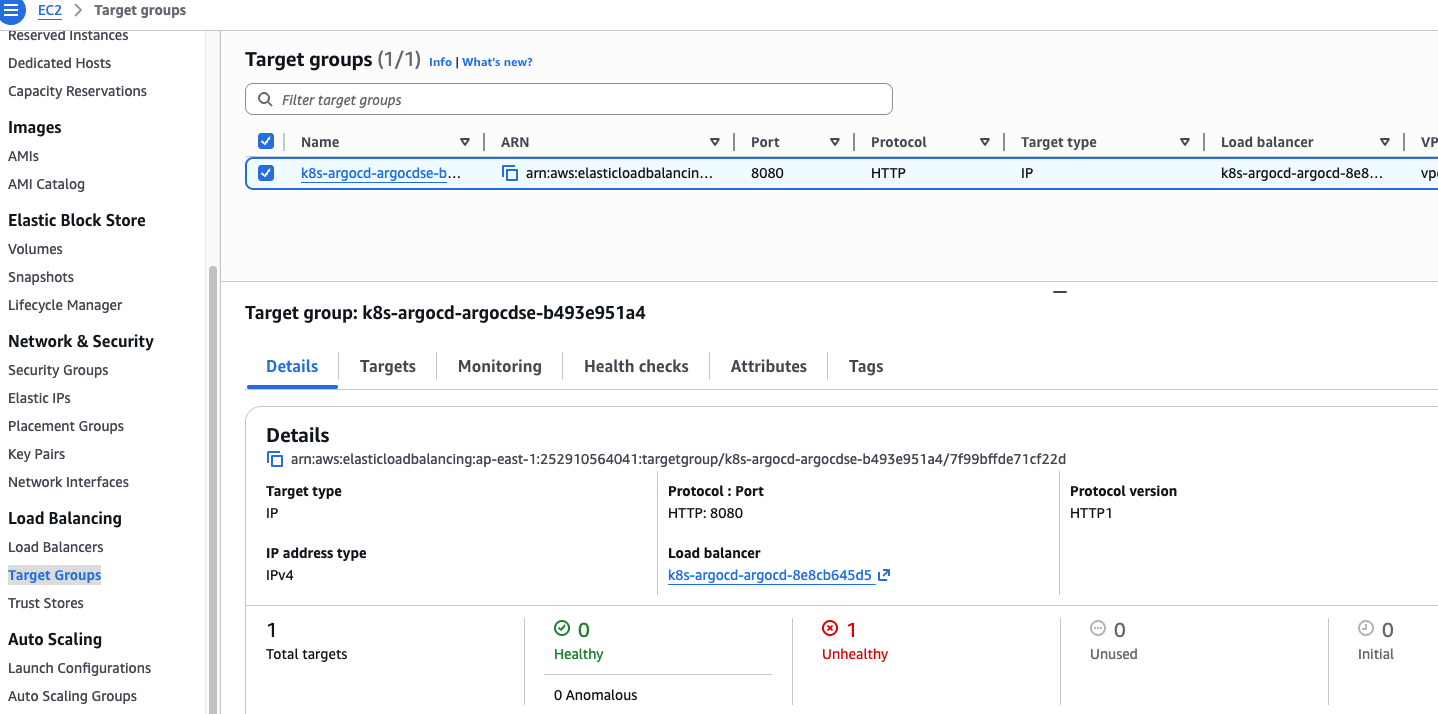
PM2
如果直接使用 node app.js 这种方式启动,会存在以下问题:
- 1️⃣ 程序崩溃自动退出,不会自动启动
- 2️⃣ 服务器重启后,程序不会自动启动
- 3️⃣ 无法负载均衡
- 4️⃣ 日志不好管理
PM2 就是为解决这些问题而生,它是 Node.js 最流行的进程管理工具 。主要负责以下功能:
| 功能 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 进程守护 | 程序崩溃自动重启 |
| 负载均衡 | Node.js 是单线程的,pm2 可以让其充分利用多核 CPU 实现多进程 |
| 日志管理 | 自动手机程序日志 |
| 开机自启 | 服务器启动自动运行 |
| 性能监控 | CPU/内存 |
| 后台运行 | 让程序以守护进程(Daemon)方式在后台运行 |
PM2 启动程序,假设程序是 app.js
pm2 start app.js --name "app-name" |
查看进程状态
pm2 list |
pm2 常用命令
程序生命周期管理
pm2 start app.js
pm2 restart app-name|all|id
pm2 stop app-name|all|id
pm2 delete app
pm2 reload <name> --update-env # PM2 会缓存环境变量。如果你修改了配置文件中的 env 变量,直接 pm2 restart 有时是不生效的。
pm2 reload all # 平滑重启, 相比 restart,reload 会逐个重启进程,实现 0 秒停机查看进程
pm2 list
日志管理
pm2 logs # 默认日志位置 ~/.pm2/logs
pm2 logs app-name
pm2 flush # 清空日志
pm2 set pm2-logrotate:max_size 10M # PM2 日志会越来越大。建议配置 日志轮转监控程序,查看 CPU/Memory 实时监控界面
pm2 monit
配置
pm2开机自启动pm2 save # 保存当前进程列表
pm2 startup # 生成启动脚本命令,复制终端弹出的那行代码并执行。
pm2 resurrect # 查看开机启动进程
PM2 集群模式
Node.js 是单线程 。PM2 可以启动 多进程利用多核 CPU 。
✔ 提高性能
✔ 提高并发
✔ 程序挂掉自动拉起
集群模式启动命令
pm2 start app.js -i max
-i max: 根据 CPU 核心数启动,如 4 vCPU 则启动 4 个 node 进程。
PM2 配置文件
生产环境一般使用 ecosystem.config.js 作为 pm2 管理配置文件来管理所有的项目,让你的部署过程 版本化、自动化、可复用 。
module.exports = { |
- 启动命令
pm2 start ecosystem.config.js
pm2 start ecosystem.config.js --env production # 启动生产环境 env
使用 PM2 配置文件时,需要注意以下事项:
集群模式(Cluster)与单实例(Fork)
如果你的应用是单机版的,没做多进程适配(例如:在内存里存 Session、使用本地变量计数),开启
instances: max会导致数据不一致。生产环境尽量使用
cluster模式以压榨多核性能,但确保你的应用是 无状态(Stateless) 的。内存溢出防御
- Node.js 程序如果不小心写了内存泄漏,长期运行会导致服务器宕机。
- 务必配置
max_memory_restart。比如你的服务器有 2G 内存,给每个实例设个 800M 左右的阈值,能有效防止全机卡死。
避免 无限重启循环
- 如果你的程序在启动阶段就报错,PM2 会疯狂尝试重启。
- 设置
min_uptime(程序运行多久才算启动成功)和max_restarts(最大重试次数),避免刷爆 CPU 和日志文件。
Watch 模式的风险
- 不要在生产环境开启
watch: true - 生产环境下任何小的配置改动或日志写入(如果路径不对)都可能触发进程重启,导致服务抖动。
watch仅建议在开发或测试环境使用。
- 不要在生产环境开启
环境变量的优先级
- PM2 会缓存环境变量。如果你修改了配置文件中的
env变量,直接pm2 restart有时是不生效的。 - 建议使用
pm2 reload <name> --update-env或直接pm2 delete后再重新start。
- PM2 会缓存环境变量。如果你修改了配置文件中的